Demystify Active Directory Certification Services (AD CS) Components
I joined SpecterOps as a Sr QA Engineer in the fall of 2024. In order to succeed in my new role, I needed to get smart on some core Identity and directory basics, quickly. If you’re newer to working with Active Directory, Azure AD / Entra ID or a hybrid environment, and the intersection of Identity and Cybersecurity, I hope this will help at a basic level. Active Directory (AD) is the beating heart of any organization. It manages user identities to enable authentication into user’s workstations and service accounts to allow access into company resources. Simply put, AD is a beast and complex domain to understand. This blog is a tl;dr about Active Directory Certificates Services (AD CS) basics and its use cases. The goal is to provide a basic knowledge of AD CS components and empower QA engineers with common terminologies
Why Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)?
PKI is essential for establishing trust and authentication in online transactions between two or more parties to ensure confidentiality and integrity of data while complying with regulations.

PKI components:
Certificate Authority (CA): The main component for issuing, revoking and managing digital certificates.
Public Key: A cryptographic key that is publicly available. The data is encrypted with public key and can only decrypted by the corresponding private key.
Private Key: A cryptographic key bonded to a specific user for decryption and digital signing. Private keys are sensitive and require a secure storage.
Registration Authority(RA): RA adds an additional layer of authentication to PKI process by verifies the identity of entities requesting digital certificates before forwarding the request to the CA for issuance.
Digital Certificate: A digital identity tied to a public key to entity’s identity, verifying its authenticity. CA issues digital certificate and contain information about the entity, as well as the public key.
Certificate Store: A centralized repository that store digital certificates and their associated properties.
Validation Authority (VA): The core function of VA is to advertise the revoked certificates through use Online Certificate Status Protocol (OSCP) or Certificate Revocation Lists (CRL). Validation Authority helps organizations to ensure that certificates have been revoked.
Hardware Security Module (HSM): A secure device to protect and manage digital keys in secure environment
Certificate Management Software: Automates tasks such as issuing, revoking, and renewing certificates to ensure the integrity and reliability of the PKI ecosystem.
All the components work together to provide a robust and secure infrastructure for online communication.
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS)
AD CS is a Windows server role that manages the lifecycle of digital certificates. Next, we will review what those features are.
Certification Authorities
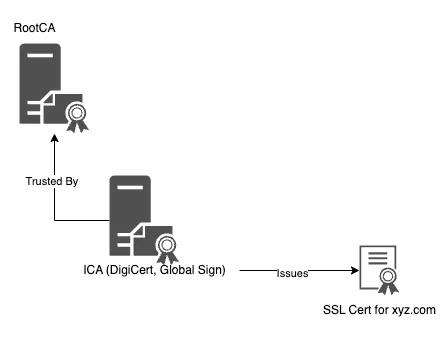
Root and subordinate certificate authorities play a crucial role in PKI hierarchy. They manage issuing, signing and storing digital certificates. The RootCA is a top level of authority that issues, signs and stores digital certificates within the domain of Active Directory forest. The RootCA is not signed by others, and it heavily relies on its own reputation hence why it’s called RootCA. Subordinate CA’s certificates are cryptographically signed by a parent CA and ultimately all CA’s certificates chain back to being signed by the RootCA. Their main responsibility is issuing digital certificates directly to end entities such as users, computers, or devices.
Online Responder
Certificates can be revoked due to too many reasons such as compromise private keys, decommissioning the service, certificate has limited validity period, misusage of the certificate to impersonate a legitimate website etc. Each Certificate Authority has a period specified when it publishes Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) and each CRL contains a serial number of the certificates, data and time it was revoked and a reason the certificate was revoked. CA publishes the CRL to a repository such as LDAP server or web server.
How the application determines if a certificate is revoked. First the application examines Certificate Distribution Point (CDP). The extension provides information about location where CRL can be obtained from either HTTP or LDAP locations. Over time CRL gets larger depending on the number of certificates issued and revoked, many clients must download CRL which has a significant impact on network performance. Responder Service is responsible to obtaining revocation status for specific certificates and a signed response sent back to the client containing the requested certificate status information.

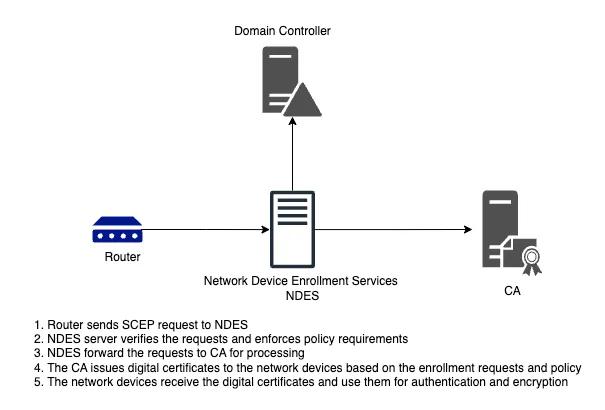
Network Device Enrollment Service (NDES)
Network device enrollment service acts as a Registration Authority (RA) to allow the software on routers and other network devices running without domain credentials to get certificates. Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) enables communication between network devices and registration authorities for certificate enrollment.
TPM key attestation
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) technology provides hardware-based and security functions through integrated cryptographic keys. For example, the scope of TPM technology is platform integrity to ensure that the boot process starts from a trusted combination of hardware and software and continues until the operating system has fully booted and applications are running. TPM key attestation prevents the certificate from being exported to an unauthorized device and can bind the user identity to the device.
Certificate Authority Web Enrollment
Certificate authority enrollment web service provides a web interface to perform certificate enrollment. The most common web enrollment cases involve renewing certificates, retrieving certificate revocation lists (CRLs), and enrolling for smart card certificates.
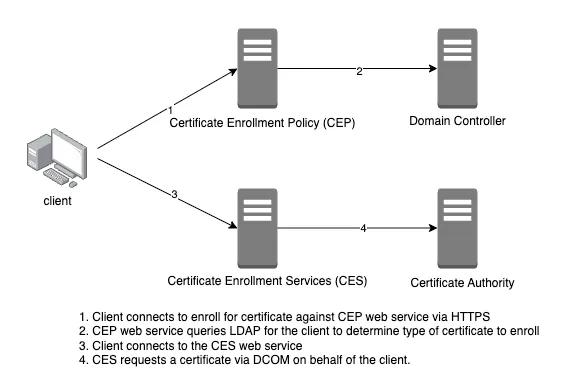
Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service
Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service enables authenticated users and computers to obtain certificate enrollment policy information. Supported authentication are:
- Windows integrated authentication (Kerberos and NTLM authentication )
- Client certificate authentication, also known as X.509 certificate authentication
Certificate Enrollment Web Service
Certificate Enrollment Web Service enables users and computers to enroll certificates via HTTPS protocol. Certificate Enrollment Web Service uses the DCOM protocol to connect to the certification authority (CA) and complete certificate enrollment on behalf of the requester.
In summary, Active Directory Certificate Services are vital in managing the certificate lifecycle to ensure secure communication, and authentication. They also allow organization to expand while improving their security posture.